Today, we will talk about the evolution of Google SERPs, the extinction of organic listings, the onrush of vertical SEO and various ways to be visible on vertical search engines.
How often do you hear questions like “How can I get first page rankings in organic SERPs?” or “How can I rank #1?” These questions are asked by many of today’s marketing managers and SEO specialists look pretty silly in the era of the Web 2.0. Why? De facto, there are no first, second and even third positions on Google organic search.
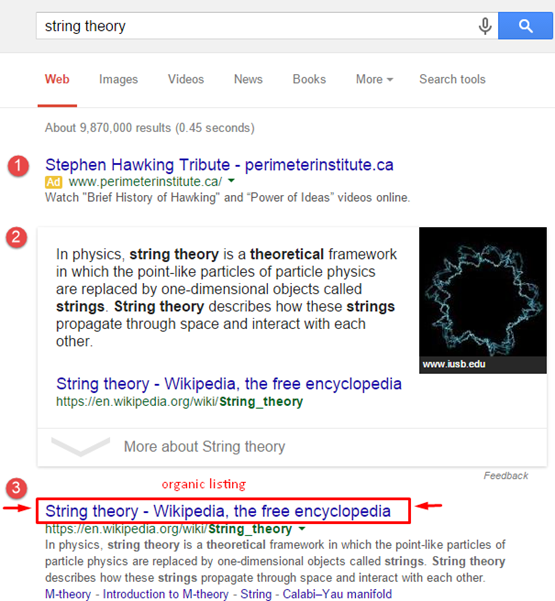
Let’s have a look at a screenshot of the first page results for a keyword “string theory” query run on my laptop (res.: 1366×729):
You can see that the first organic listing (for a Wikipedia article) occupies only the #3 spot, but positioned by Google as the #1 ranking position. Organic listings are followed by image and video results. Totally we have 12 result positions per page and 8 of them are organic. So what is going on with organic search? It seems obvious that, under the guise of high-end user experience, Google is taking searchers away from organic search and pushing them to click more on paid (Google AdWords) vertical search results or Google products (Google Maps, Google Play Apps), or default (knowledge graph and direct answer boxes) listings which are all incorporated into a universal search results set.
For those who are not familiar to the concepts of organic, vertical and universal search, let’s go over this. We have Google search results that are split into Organic, Universal and Vertical SERPs.
Organic search returns naturally generated web page listings that are relevant to this or that search term.
Universal Search provides you with a blended set of organic listings (content sites), paid results (ads) and specialized results (video, maps, images, news, deep articles etc.) delivered for a given query.
Vertical Search returns specialized results which represent different types of content for a query. You can search for images in Image Search, for videos in Video Search, for news in News Search, and local shops or restaurants in Maps Search or specific search engines like Yelp, Open Table etc. Vertical results are returned by Google within universal search results.
Vertical search platforms are the new intermediaries for searchers to complete their desired actions, be it informational or transactional intent. Vertical search has a lot of advantages over universal search:
– There may be a specialized type of content wanted
– A faster indexation occurs
– There will be less competition within a specific category
– More accurate results ensue
Even taking all the advantages into account, there are no guarantees that you will get high rankings in vertical search. The problem is that some really big vertical sharks (producers or curators of content) who have gotten their teeth into their niche-specific traffic pie, which benefits them with direct traffic to their platforms. On YouTube, there are channels that practically own certain categories in terms of YouTube search results. Outside Google, searches are conducted directly on Amazon, eBay, Craigslist, Kayak, Trip Advisor, Yelp, Open Table etc. With the popularity of some vertical sites and platforms, Google loses a lot of search traffic. No wonder that Google wants to make an aggressive effort to retain users by providing them with more exciting search listings, including knowledge Graph, Direct Answers, Google Map and Places results etc.
Such a difficult multi-layered Google ecosystem structure didn’t happen in a clap. It took more than 20 years for Google to build the current search experience with a strong algorithmic ranking system and a user-friendly interface. Let’s take a glance at the evolution of Google search results.
Evolution of Google Search
1996 – Google’s birth as a research project.
2000 – Google launched Google AdWords and incorporated ad results next to organic SERPs.
2001 – Google launched Image Search with more than 250 million images available. In 2012 Google updated its image search engine by providing users with an image search where you drag and drop an image into the query field.
2002 – Google News was launched with 4,000 news sources.
2002 – Google launched Froogle (Lately renamed Google Shopping).
2004 – Google introduced Google Local with relevant neighborhood business listings, maps, and directions. Today, organic local listings are combined with Google Maps, a Local Carousel and local pack results.
2005 – Google added a Weather box and a “Google Q&A” box with direct facts on famous people, planets, places and landmarks, movies etc. Today, Google provides direct answers for many queries.
2007 – Google introduced universal search with verticals for video, news, books, image and local search results all integrated together into a single search result page.
2010 –Google Instant (lately Google Auto-Suggest) had been added. It supplies users with relevant suggested search queries as you type so you can quickly find what you need.
2012 – Google Knowledge Graph was launched.
2013 – Google announced app indexing.
The behavior of Internet users who conduct searches on Google has also changed drastically. In 2005, searchers viewed fewer search results but spent more time on each listing (circa 2 sec), while in 2014, searchers viewed more search results but spent less time on each listing (circa 1.17 sec). It means that users’ search behavior is tending towards vertical thinking and scrolling, especially when it comes to mobile search.
3 arguments in favour of Vertical SEO
In the course of Google SERP evolution, the term “organic listings” has become subtle, giving way to vertical, paid and default search results.
- Less than 15 % of purchase-oriented searches are run on classic search engines.
- By the end of 2014, 39 % of U.S. online shoppers started their purchase process searching on Amazon, while only 11 % of buyers did their transactional search on Google.
[Tweet “Less than 15 % of purchase-oriented searches are run on classic search engines. 39 % of U.S. online shoppers started their purchase process searching on Amazon. Only 11 % of buyers did their transactional search on Google. “]
5 Vertical Search Engines you need to optimize your content for.
There are many kinds of vertical search engines you can and should optimize your content for. However, there are several core vertical search engines you should generate and optimize your content for.
- Image Search Optimization
Considering that image search is the most popular vertical after web search, one cannot miss the opportunity to win additional traffic and rankings on image search engines. There is a classic Google Image Search and there are vertical websites and mobile app platforms which have a huge number of active users continuously growing at an exponential rate. Pinterest and Instagram are perfect image platforms for you to raise your brand awareness and lead generation. Here is a handful of useful SEO guides for Pinterest, Instagram and Google image optimization.
- Video Search Optimization
Videos are as popular as images and have their own rules for optimization. Everybody knows that Google Video Search is the synonym for YouTube Search. This is in fact the №2 largest search engine in the world, so you need to make every effort to succeed on YouTube and win more rankings on its engine for your top performing keywords. Here is a detailed list of advanced SEO tactics to become a million view leader on YouTube.
- Apps Search
Today, in the era of mobile-friendly web search, the App Store Optimization (aka ASO) should be one of your top-level priorities on the way to website search engine domination. Make sure you have an effective ASO strategy following the ultimate guide to App Store Optimization.
- Local Search
Local businesses can generate effective revenue only when business owners know the fundamentals of local SEO (these drastically changed after the Google Pigeon Update) and apply them for the effective online promotion of their product benefits. With this Local SEO Guide you can learn some of the core principals of up-to-date local SEO for small and medium businesses.
- Shopping Search
Shopping is the most competitive market of all. If you run or plan to start your online business in this niche, you should be ready to compete with such mighty beasts as Google with its AdWords and its upcoming shopping platform, Amazon and eBay. You can benefit from running your advertising campaigns with the help of Google Adwords and selling your products via Amazon or eBay. Since Amazon and eBay are search engines themselves with their own system of SEO factors and hierarchies, you should take a nuanced approach to their vertical shopping SE optimization. While optimizing your eCommerce site, be sure to provide an intuitive, mobile-friendly interface and usability, since this is what makes Amazon and eBay do better than Google and other competitors.
What are medium sources I can benefit from other than Google and the leading vertical websites?
Optimizing for each of the verticals and for Google organic search may seem frustrating and time-consuming.
The SERPs game may take a lot of your effort to become a lord of the SERP kingdoms (Search Engine Result Page Kingdoms). But you should not forget that you can become a popular brand and attract a lot of traffic via alternative digital mediums like email marketing, social media marketing/remarketing, blogging and native advertising etc. For example according to research in 2013, 44% of email subscribers made at least one purchase via commercial newsletter.
Is it possible to track all of my multi-vertical rankings from one single dashboard?
With Web CEO you can easily monitor your ranking success thanks to the cross-channel integration of most search engine verticals, including organic, paid, local, YouTube and image. Try the WebCEO Rank Checker for free in order to see how vertical search affects your rankings and traffic.